Buying Guide for Scooter Forks
Prepare for our extensive guide on purchasing pro scooter forks. We will discuss all crucial aspects to consider before selecting a new freestyle scooter fork. Among these are compatibility, wheel sizes, wheel offset, and more.
A perfectly tuned pro scooter requires an excellent fork. Scooter forks are vital for securing the front wheel, and your fork’s specifications dictate the wheel sizes you can install – regarding both wheel width and diameter. Stick around for some valuable tips on stunt scooter forks!
Overview
Understanding the Basics of Scooter Forks

The fork extends through the headset and into the headtube of your deck. The front wheel attaches to the fork, with the compression system, clamps, and bars mounted on top. Your fork plays a substantial role in your entire setup as it specifies the size of wheels you can place on your scooter.
Nowadays, most scooter forks are produced from a single aluminium piece, enhanced through different heat treatments. Threaded scooter forks made of steel were prevalent but are now outdated due to being heavier and less durable.
Scooter forks compatible with SCS, HIC, and IHC include a built-in starnut within the fork tube. The compression bolt screws into this starnut during the installation of the compression system.
ICS configurations differ because, with ICS, the starnut goes inside the bar, and the compression bolt is inserted through the bottom of the fork before wheel installation. If uncertain about which compression system you are using, it’s advisable to review our detailed guide:
Weight, wheel size, wheel offset, and compression are the essential elements to evaluate when buying a new scooter front fork. This guide thoroughly examines these topics.
We consistently have top-grade scooter forks from leading brands in the market, and we probably have one that fits your requirements. If you are ready to decide, we invite you to explore our range of high-quality forks for pro scooters:
Scooter Forks and Wheel Dimensions

When acquiring a new fork for your scooter, always confirm its compatibility with the wheels. Pair the wheel size concerning diameter and width. Specifically, ensure the wheel diameter does not surpass the largest wheel diameter designated for the fork. Also, confirm that the wheel hub's width is either matching or smaller than the fork’s specified wheel size.
Wheel Diameter
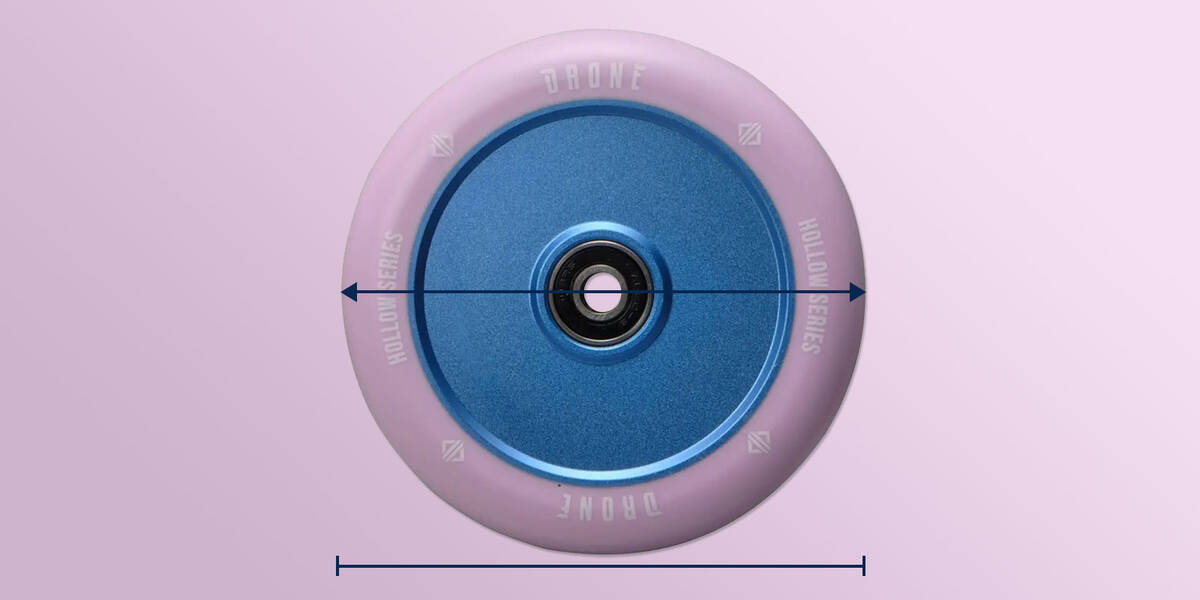
Most scooter forks support wheel diameters of 110 mm, the prevailing wheel diameter. Nevertheless, numerous forks can host scooter wheels as large as 125 mm. Just check that your wheels remain within the fork's capacity, and you'll be set.
For instance, if you’re utilising wheels with a 115 mm diameter, it’s crucial to verify if your fork can handle wheels of that size or bigger.
Wheel Core Width
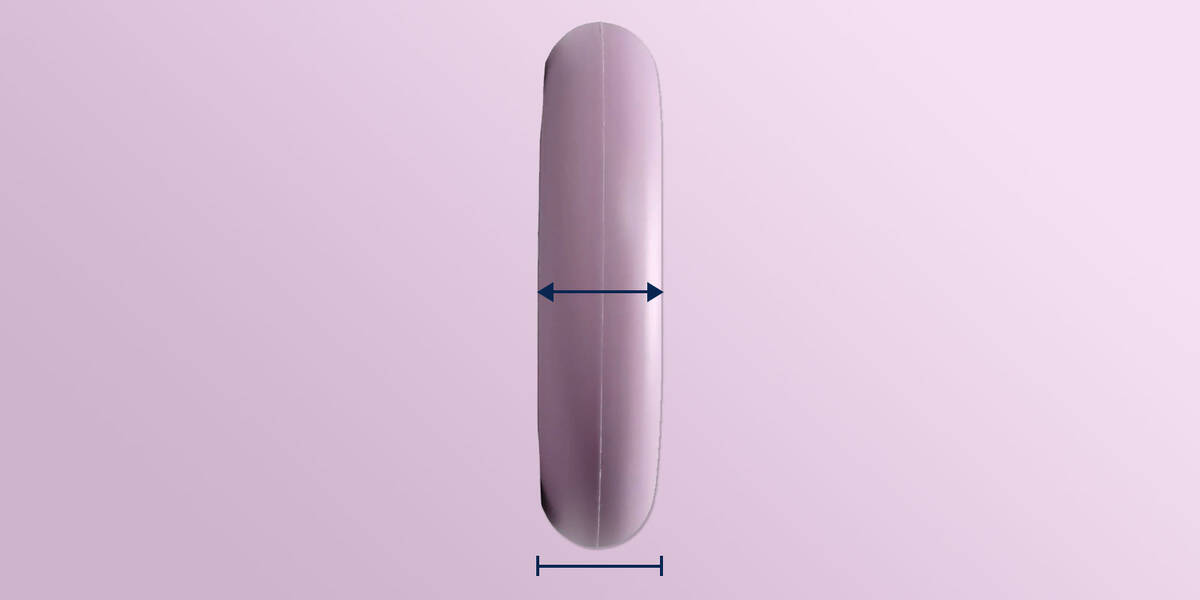
Scooter forks are crafted to fit wheels of particular widths, generally between 24 to 30 mm. Within this range, we see scooter wheels with widths of 26 and 28 mm.
Commonly, scooter forks come with spacers so that a fork designed to hold 30 mm wide wheels can also fit 24, 26, and 28 mm wheels when the correct spacers are in place.
Wheels narrower than a scooter fork's maximum wheel hub width can be mounted, although if the wheel is broader (e.g., a 30 mm wide wheel for a 24 mm wide fork), it would not fit.
Diameter and Length of Fork Axle

The typical wheel axles for scooters have a diameter of 8 mm, but some forks also work with scooter wheel axles having a 12 mm diameter. For scooters, the usual bearing size is 608 bearings, which accommodate an 8 mm axle diameter. Forks compatible with the 12 standard typically include 8 mm adapters so you can use standard 8 mm axles, too.
The correct axle length relies on your scooter fork's width. You need an axle that extends at least as long as your fork’s width, measured externally.
Defining a 12 Standard Scooter Fork
12STD scooter forks are engineered to fit wheel axles with a 12 mm diameter. Such a large axle diameter requires looking for the 6001 bearing size.
A 12-standard pro scooter configuration usually features bigger and wider wheels. Generally, a 12STD pro scooter setup promises increased speed, stability, and durability, but these benefits arise with added weight and reduced agility.
Numerous 12 standard forks supply spacers allowing the fitting of 8 mm axles and regular 608 bearings on the fork.
If switching to 12STD, you must be aware that beyond the 12STD fork, wheels fitting 6001 bearings and a deck capable of accommodating larger wheels and wheel axles are necessary. You will find everything you need in our range:
Wheel Offset on Pro Scooter Forks

Wheel offset, indicated in millimetres, refers to the distance from the centre of the fork's turning axis to the wheel axle, also known as the rake. It signifies how much the wheel is positioned in front of the fork.
This offset significantly impacts your scooter's stability and agility, as it lengthens the wheelbase (the distance between the front and back wheels).
A 10 mm wheel offset is most typical. It enhances stability and control across your setup, simplifying and rendering steering more predictable.
Zero-offset forks are particularly agile and responsive. With no offset, the front wheel is nearer to the rider, enhancing the scooter’s agility and responsiveness. Nose manuals become easier with zero-offset forks due to the rider's feet being closer to the ground, improving balance. Foot jams are also simpler to execute since a larger part of the wheel aids in jamming.
Scooter Forks & Compression Systems
Forks for SCS and HIC compression are identical. They possess a starnut inside the fork tube where a compression bolt fastens. The primary difference lies in the compression elements encircling the forks: SCS employs an SCS clamp, while HIC utilises an HIC shim.
IHC compression forks have a slimmer fork tube, making them ideal for riders who focus on minimising the overall weight of their setup. Typically, IHC forks represent the lightest scooter forks.
- SCS Scooter Forks: Standard & oversized bars without slits and standard or oversized SCS clamps
- HIC Scooter Forks: Oversized bars with slits and oversized non-SCS clamps
- IHC Scooter Forks: Standard-sized bars and standard-sized non-SCS clamps
In ICS and ICS-10 compatible forks, the compression bolt is mounted from the base of the fork into a starnut located inside the bars. While ICS configurations are infrequent in custom-built scooters, they are renowned for being exceptionally lightweight compared to other compression systems.
If there is any uncertainty about compatibility across different forks, these guides might be useful:
